About Digital Literacy
Digital literacy is the ability to effectively and critically
navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital technologies. It
encompasses a wide range of skills and competencies that are essential for
functioning in today's digital age. As an academic subject, digital literacy
is often taught in educational institutions to equip students with the
necessary knowledge and skills to use digital tools and resources
effectively.
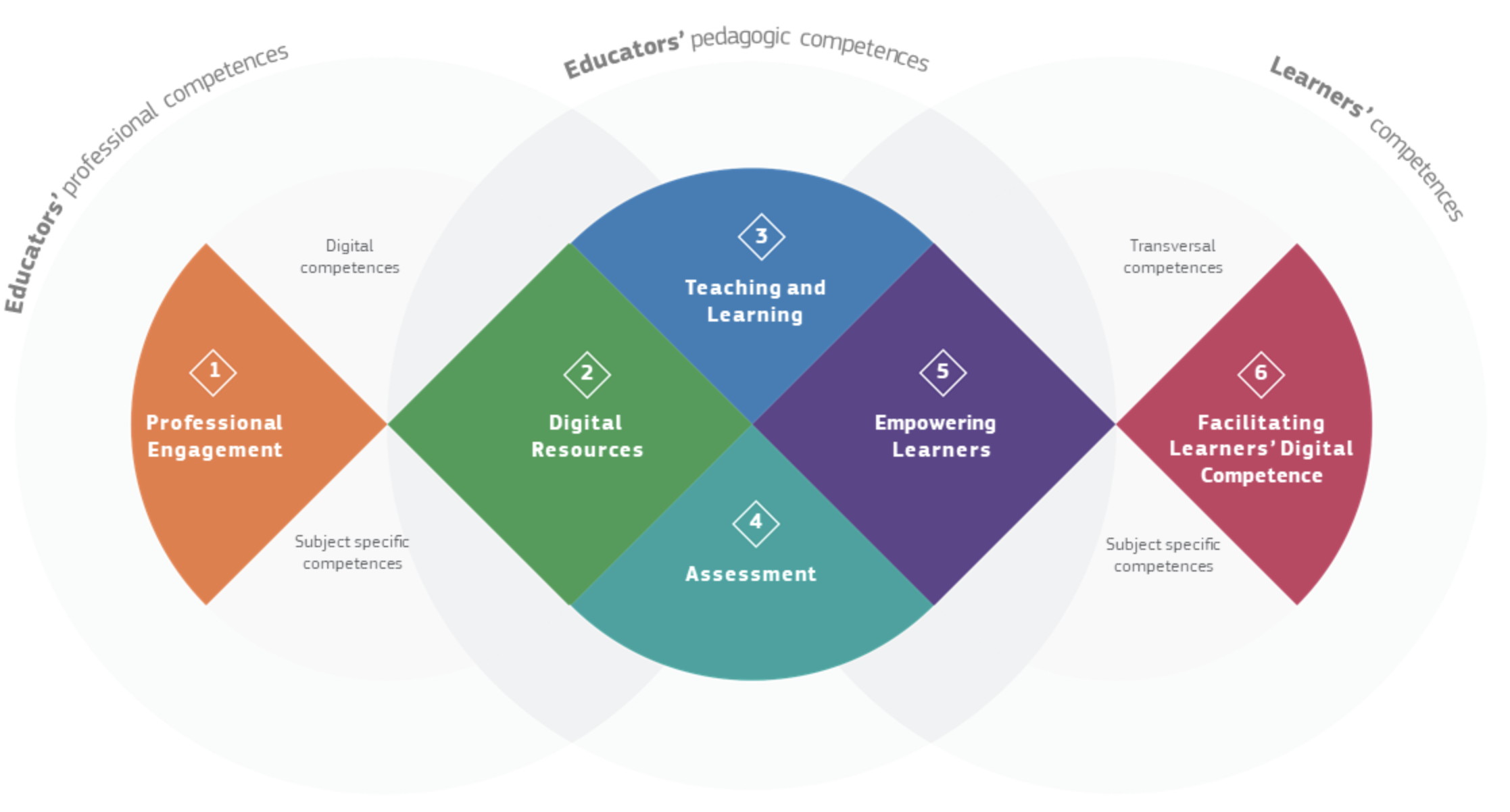 Figure 1. The European Framework for the Digital Competence of
Educators (DigCompEdu)
Figure 1. The European Framework for the Digital Competence of
Educators (DigCompEdu)
The
European digital competency framework (Fig. 1) identified six categories for
educator competencies, including:
- Professional engagement
- Digital resources
- Teaching and learning
- Assessment
- Empowering students
- Facilitating students’ digital competence.
This survey is an adaption of the European Framework for the Digital Competence of
Educators and explores your use and understanding of digital
technologies. The survey will take about 30 minutes to complete. Use the
tabs above to navigate
through all the survey sections. A report will display once you have completed all the questions.
Note:If you come across a word you don't know, you can quickly look up dictionary definitions. Just double-click the word.
Note:If you come across a word you don't know, you can quickly look up dictionary definitions. Just double-click the word.